This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
NetSuite offers two different types of User Licenses: Full Access Users and Employee Center Users

When it comes to the types of NetSuite User Licenses, there are two: Full Access Users and Employee Center Users. Full Access Users have general access to NetSuite, and can be assigned many roles. Employee Center Users, however, have very limited access to NetSuite. These users primarily use NetSuite for time and expense entries, but they can also enter and approve purchase orders. Employee Center Users are also able to approve vendor bills, but are not able to enter them.
Let’s break down the differences with user access.
What is a role?
A role is a defined access configuration. This is important to keep in mind when trying to figure out what role would be most suitable for a new employee. In NetSuite, there are either Standard Roles, or Custom Roles. A Standard Role is a template role that is not customizable, and likely directly relates to employee positions, such as an Accountant, or a Sales Representative. If you are looking to customize a role for an employee, you can choose Custom Role when setting them up. This will still allow you to make permission changes to users’ assigned roles as needed. This is important because the ability to modify a role without having to change multiple users’ role assignments simplifies the maintenance process. Many roles can be assigned to the same user, and changes can be made to their assigned roles as necessary.
The different roles of Full Access Licenses
The Administrator Role
This role is very powerful, and is recommended that at least 2 employees at the company have this access just in case someone leaves, or is not available during a crucial time. Because a Full Access License is required for an employee to be assigned to this role, the user has the ability to utilize all tasks and pages in NetSuite, including having full visibility in to all areas of the NetSuite Environment, as well as full access to the Setup Manager. As of NetSuite 2018.1, Administrators must use two-factor authentication in accounts that were newly provisioned.
One more thing to note about the Administrator Role in NetSuite, is that since it is a Standard Role, it is not customizable. If you had plans to assign this role with customizations, a workaround would be to create and use a custom administrator role rather than the standard one. NetSuite also recommends that you use Core Administration Permissions to allow you to configure a role that behaves like the standard Administrator role, but has limited access to certain sensitive information. These limitations are made up of permissions that mirror the behaviors that are accessible to those assigned an Administrator Role. According to NetSuite, Core Administration Permissions can be assigned to any role and restricted through role configuration.
The main differences between the Core Administrator Role and the Administrator Role are:
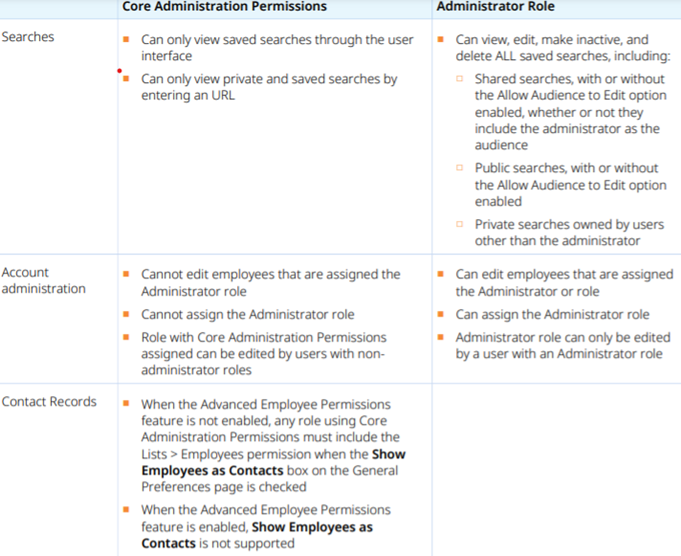
Other Administrative Roles
There are options to allow employees to have administrator roles, in more localized areas of NetSuite, such as the Issues Administrator, Marketing Administrator, and Sales Administrator roles. These more specific administrator roles do not have the same capabilities as an employee that was assigned a standard Administrator Role, but grant additional access where needed.
How to Customize and Create a Role according to Oracle NetSuite’s Whitepapers:
To begin customizing or creating a role:
- To customize a standard role, go to Setup > Users/Roles > Manage Roles, and on the Manage Roles page, click Customize next to a standard role. This type of custom role inherits all of the standard role’s permissions to start; you can make changes as necessary.
- To create a new role that does not start with a list of associated permissions, go to Setup > Users/ Roles > Manage Roles > New. Entering Basic Role Information 1. In the Name field, enter a name for this custom role. This name should be easy for you to recognize when assigning it to users. 2. If you use scripting, you can optionally enter an ID used for this role in scripts.
- If you are creating a new role, select the center type to base the role on. The center type sets default permissions and access levels that you can customize below. (If you are customizing a standard role, the center type is predefined.) After you enter basic information for the role, set optional restrictions for the role.
Employee Center Licenses
These NetSuite Users are not required to have roles within NetSuite, and they have very limited functionality. Access for Employee Center Users is strictly limited to entering Time & Expense, for daily work and on projects, Entering and Approving Purchase Orders, as well as Approving Vendor Bills. Employee Center Users are not able to Enter Vendor Bills. This user does not have general access to functionalities within the CRM or ERP, so they are not able to alter the NetSuite Environment in any way, and are not able to pull vital reports such as financials or employee information. Employee Center Licenses are sold in packs of 5, and since the users have limited functionality, licensing five employees with this user is about the same cost as purchasing one Full Access License.
Most companies, depending on size and need, utilize a combination of both the Full Access and Employee Center Access Licenses for business productivity.
Have any questions about which types of NetSuite User Licenses will work best for your employees? Please contact us at any time.
This publication contains general information only and Sikich is not, by means of this publication, rendering accounting, business, financial, investment, legal, tax, or any other professional advice or services. This publication is not a substitute for such professional advice or services, nor should you use it as a basis for any decision, action or omission that may affect you or your business. Before making any decision, taking any action or omitting an action that may affect you or your business, you should consult a qualified professional advisor. In addition, this publication may contain certain content generated by an artificial intelligence (AI) language model. You acknowledge that Sikich shall not be responsible for any loss sustained by you or any person who relies on this publication.




