More than 20% of the U.S. population will be over the age of 65 by 2050. Currently, one in five people in the U.S. receive social security benefits. Below, we explore the basics of social security to support you as you plan for retirement.
Background
Social security was started in 1935 by President Roosevelt and was designed to pay retired workers a continuous income starting at age 65. Flash forward to now, social security covers not just retirees’ income, but also survivors’ insurance, disability insurance, Medicare and Supplemental Security Income.
Eligibility
In order to be eligible to receive social security benefits, you need 40 credits, where one credit is equal to one quarter of work (quarters do not need to occur consecutively). An individual that works for 10 years can earn 40 credits.
You are eligible to receive the Primary Insurance Amount (PIA) at Full Retirement Age (FRA) once you’ve hit this credit milestone. Your PIA is based on the highest 35 years of earnings history while working, and your FRA is determined based on when you were born. Note that the FRA is 66 years and two months for anyone born in 1955, and the FRA increases from there to age 67 for people born in 1960 or later.
In 2022, the maximum monthly benefit at FRA is $3,345. Most retirees do not receive the maximum benefit, and the average monthly benefit is $1,657. To view your PIA, you can establish a free account at https://ssa.gov/myaccount; however, you will receive an annual statement in the mail as well.
Exceptions
Anyone age 62 or older can claim reduced benefits from social security. When the early benefit is started, the benefit remains at the reduced level indefinitely. Likewise, you can defer starting benefits to age 70. Benefits that are deferred receive a higher rate than the PIA.
For example, a worker born in 1959 has an FRA of 66 years and 10 months. This worker has a PIA of $1,000 per month.
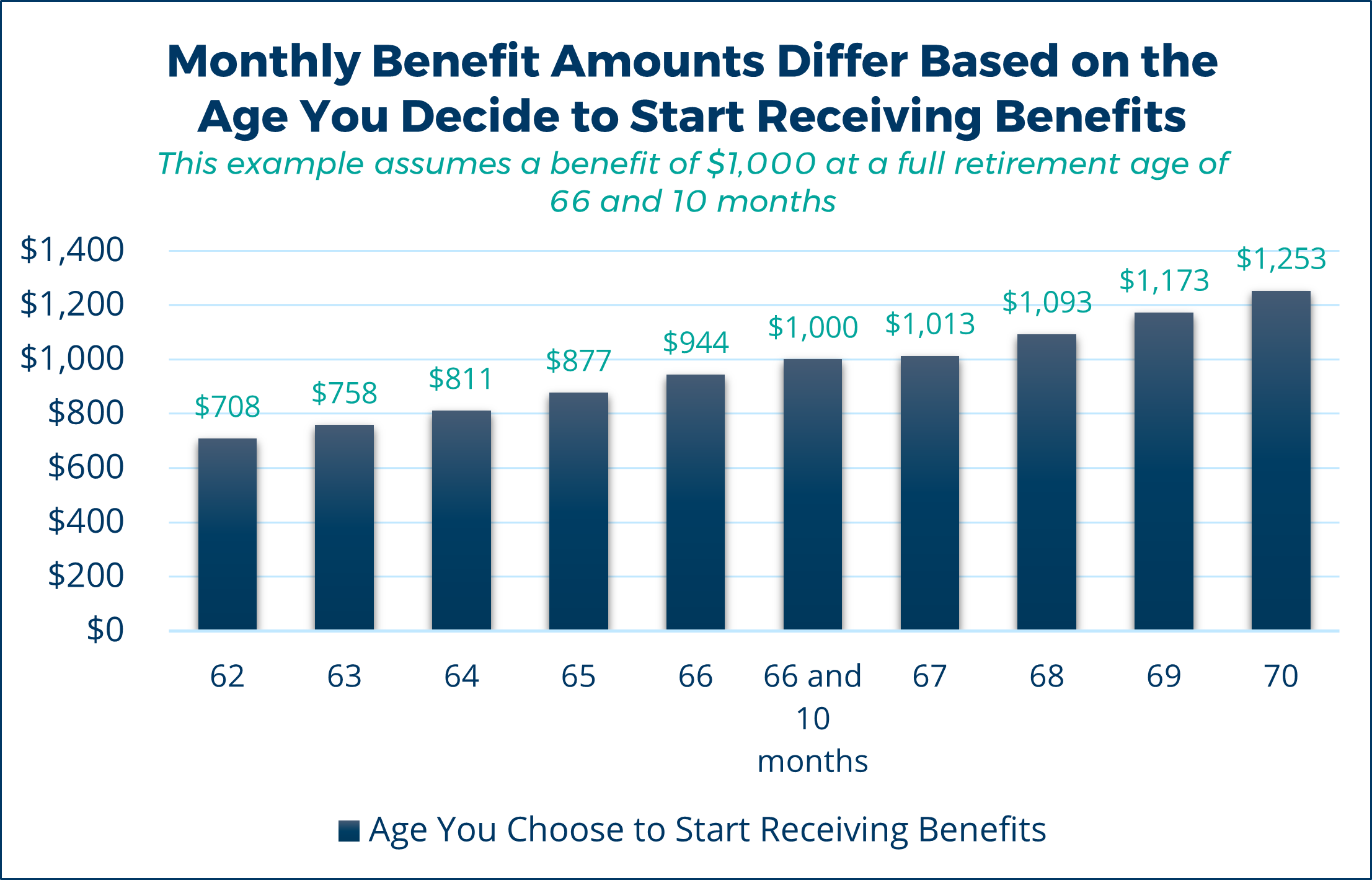
If this worker decides at age 62 that funds are needed right away, they can decide to start social security benefits at the reduced amount of $708. The benefit does not increase to the full amount when the individual reaches the FRA. It should be noted that starting benefits closer to the FRA will allow for greater benefits – so postponing as much as possible has its advantages.
On the other hand, each year deferred is equivalent to an 8% increase on the PIA amount. If this individual continues to work past the FRA, the benefit can be deferred and the employee can receive a maximum benefit of $1,253. This higher benefit is also permanent.
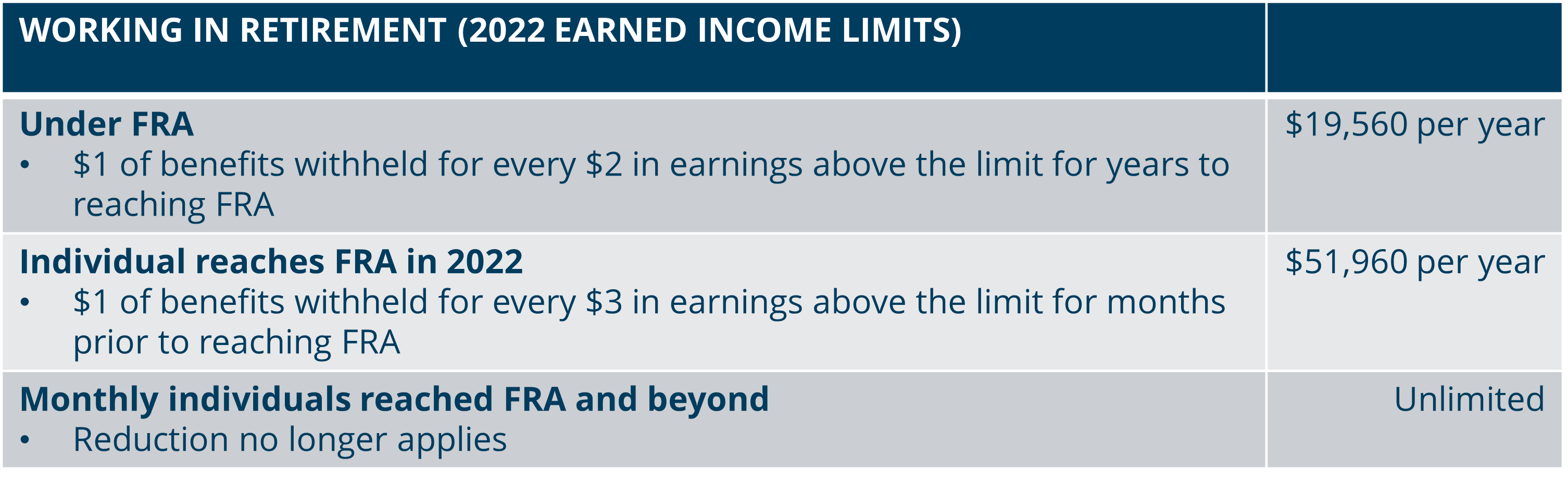
Please note: when a worker elects to receive benefits prior to the full retirement age, there are earning limits. If you earn beyond the limit, the benefit is further reduced from the already lowered amount. View the chart below for an illustration.
Social security is an important component of your retirement income but should not be viewed as your only source. As you plan for retirement, social security and when to start benefits should be part of your overall financial plan.
Contact us if you have any questions, and we’ll be in touch.
Resource:
“Status of the Social Security and Medicare Programs: A Summary of the 2021 Annual Reports,” Social Security and Medicare Boards of Trustees, 2021.
This publication contains general information only and Sikich is not, by means of this publication, rendering accounting, business, financial, investment, legal, tax, or any other professional advice or services. This publication is not a substitute for such professional advice or services, nor should you use it as a basis for any decision, action or omission that may affect you or your business. Before making any decision, taking any action or omitting an action that may affect you or your business, you should consult a qualified professional advisor. In addition, this publication may contain certain content generated by an artificial intelligence (AI) language model. You acknowledge that Sikich shall not be responsible for any loss sustained by you or any person who relies on this publication.









